Crop Diversification
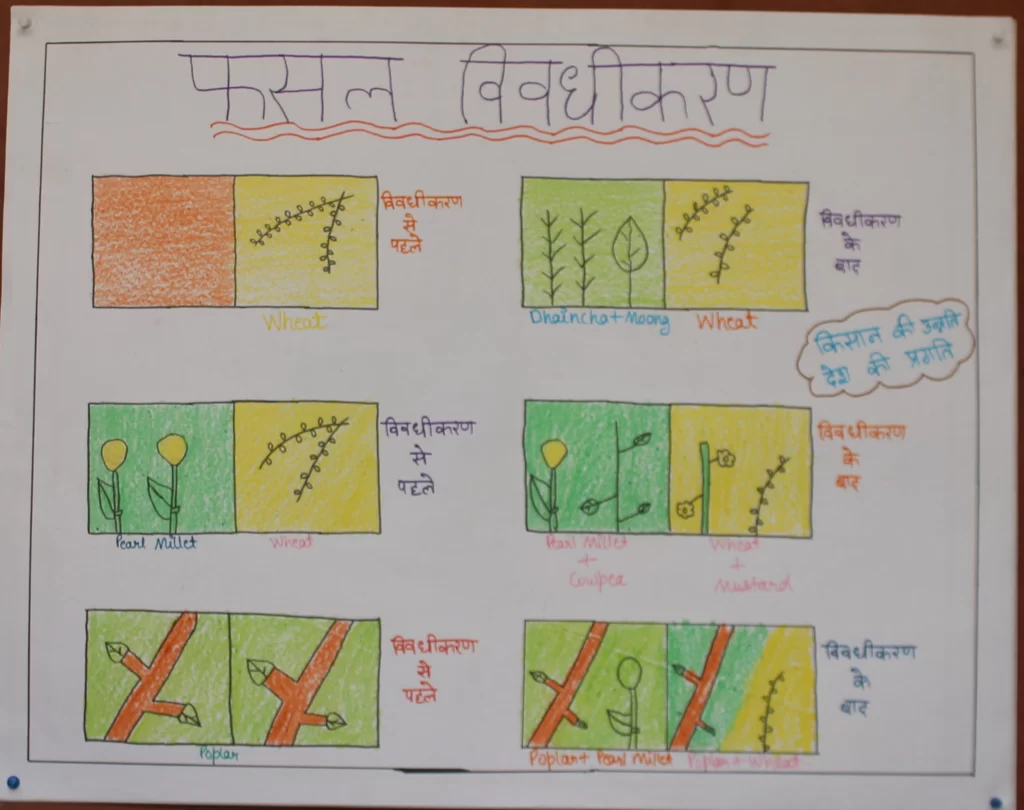
Crop diversification is the practice of growing a variety of crops in the same area or on the same farm. This approach differs from monoculture, which involves growing a single crop over a large area. Crop diversification is important for several reasons:
- Resilience: Crop diversification helps to make farms more resilient to weather, pests, and other factors that can affect crop yields. By growing a variety of crops, farmers can reduce their risk of losing their entire crop to a single event, such as a drought or disease outbreak.
- Soil health: Planting a variety of crops can help to improve soil health by reducing soil erosion, increasing soil organic matter, and enhancing nutrient cycling. This can lead to more sustainable farming practices and better crop yields in the long run.
- Economic benefits: Diversifying crops can provide economic benefits to farmers by reducing their dependence on a single crop and providing a more stable source of income. By growing a variety of crops, farmers can also take advantage of market opportunities for different crops and reduce their exposure to price fluctuations in any one crop.
- Environmental benefits: Crop diversification can have environmental benefits by reducing the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, increasing biodiversity on farms, and reducing the carbon footprint of agriculture.
Overall, crop diversification is a key strategy for promoting sustainable agriculture and improving the resilience and productivity of farms. By growing a variety of crops, farmers can promote soil health, reduce risks, and benefit economically while also contributing to a more sustainable and resilient food system.
